GRAVIMETRY
Gravimetric prospection is a geophysical method based on the study of undersoil properties through measure and analysis of the gravitational field on the surface of the crust.
It consists of a highly precise measure of the acceleration of gravity in different points, registering abnormal variations which could be interpreted as changes in the soil density. When studying gravitational field distribution, disturbances, which are gravitational anomalies related to the mass distributions of the geological bodies.
With appropriate mathematical models, they allow to get to know in quantity the density contrasts and geometry of the disturbance bodies.
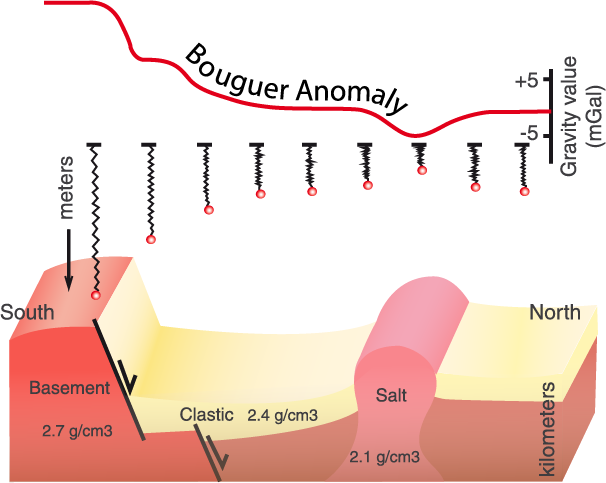
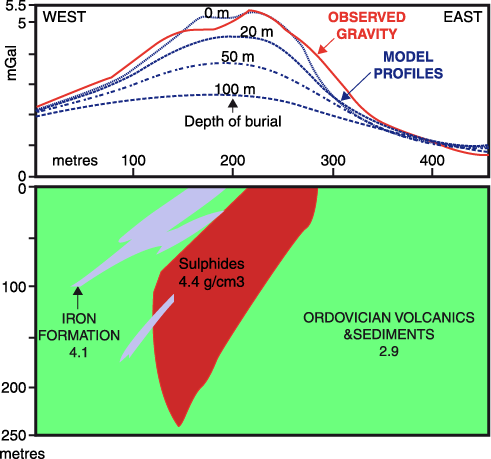
These could be magnetic intrusive bodies, lithological limits, sedimentary mining area, crust thickness changes. In applied geophysics, gravimetry applies to the exploration of the layers near the surface, for example, in the exploration of hydrocarbon, metal deposits (as an example of sulphide mineral body in figure …) and no metallic raw material, in hydrogeology and environmental studies.
It consists of a highly precise measure of the acceleration of gravity in different points, registering abnormal variations which could be interpreted as changes in the soil density. When studying gravitational field distribution, disturbances, which are gravitational anomalies related to the mass distributions of the geological bodies.
With appropriate mathematical models, they allow to get to know in quantity the density contrasts and geometry of the disturbance bodies.
These could be magnetic intrusive bodies, lithological limits, sedimentary mining area, crust thickness changes. In applied geophysics, gravimetry applies to the exploration of the layers near the surface, for example, in the exploration of hydrocarbon, metal deposits (as an example of sulphide mineral body in figure …) and no metallic raw material, in hydrogeology and environmental studies.
MAIN APPLICATIONS
- Hydrocarbon location
- Search and location of tunnels and cavities
- Archeological investigation
- Structural and scientific studies of the crust
- Oilshed studies and base depth
Geofísica Argentina © - 2015 - (All rights reserved)
Address: Bº UDAP II Mna F C17 - Rivadavia - San Juan - Argentina
Phone numbers:
+54 9 264 4854870 - +54 9 264 5883048 - +54 9 264 5318547
E-mail: info@geofisicaargentina.com
Address: Bº UDAP II Mna F C17 - Rivadavia - San Juan - Argentina
Phone numbers:
+54 9 264 4854870 - +54 9 264 5883048 - +54 9 264 5318547
E-mail: info@geofisicaargentina.com
Web design: Pica Estudio




