GROUND PENETRATING RADAR (GPR-GEORADAR)
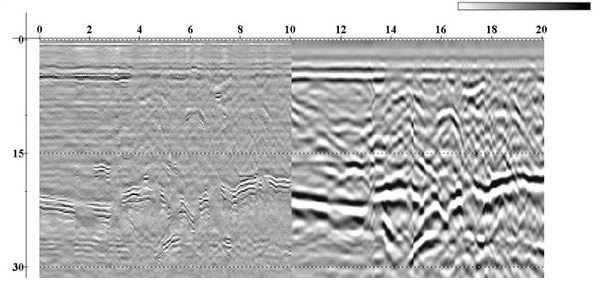
Georadar is a geophysical prospection method based on the emission of short-time electromagnetic impulses in the frequency band UHF-VHF (between 20 MHz and 2, 5 GHz.) Thanks to a transmitter, a train of impulse waves EM is generated, which, when crossing different undersoil layers, causes a reflection on the energy wave front. The receptor detects then these reflections generating a register or two-dimensional image of the undersoil along all the antennae movement line.
The GPR has achieved to obtain good soil definitions due to the high frequencies that it works with, and to the contrasts of the materials’ dielectric permissiveness.
The GPR has achieved to obtain good soil definitions due to the high frequencies that it works with, and to the contrasts of the materials’ dielectric permissiveness.
 Georadar
GeoradarMAIN APPLICATIONS
- Water and gas pipes detection, electric and telephone wire
- Sewage system location
- Holes in the ground location
- Geotechnical studies
- Sounding studies to determine breakings and foundations
- Geological exploration
- Glacial investigation
- Sedimentary layers study
- Non-destructive studies of concrete structures
- Bridgeboard inspection
- Reinforcement bars location in concrete structures
- Buried tanks and deposits location
- Buried bodies location
- Burying zone limitation
- Buried mines and grenades, shells location
- Search for buried weapons
- Concrete layer’s thickness measure (which forms the road surface) with respect to quality
- Geotextile inspection
- Archaeology
Geofísica Argentina © - 2015 - (All rights reserved)
Address: Bº UDAP II Mna F C17 - Rivadavia - San Juan - Argentina
Phone numbers:
+54 9 264 4854870 - +54 9 264 5883048 - +54 9 264 5318547
E-mail: info@geofisicaargentina.com
Address: Bº UDAP II Mna F C17 - Rivadavia - San Juan - Argentina
Phone numbers:
+54 9 264 4854870 - +54 9 264 5883048 - +54 9 264 5318547
E-mail: info@geofisicaargentina.com
Web design: Pica Estudio




